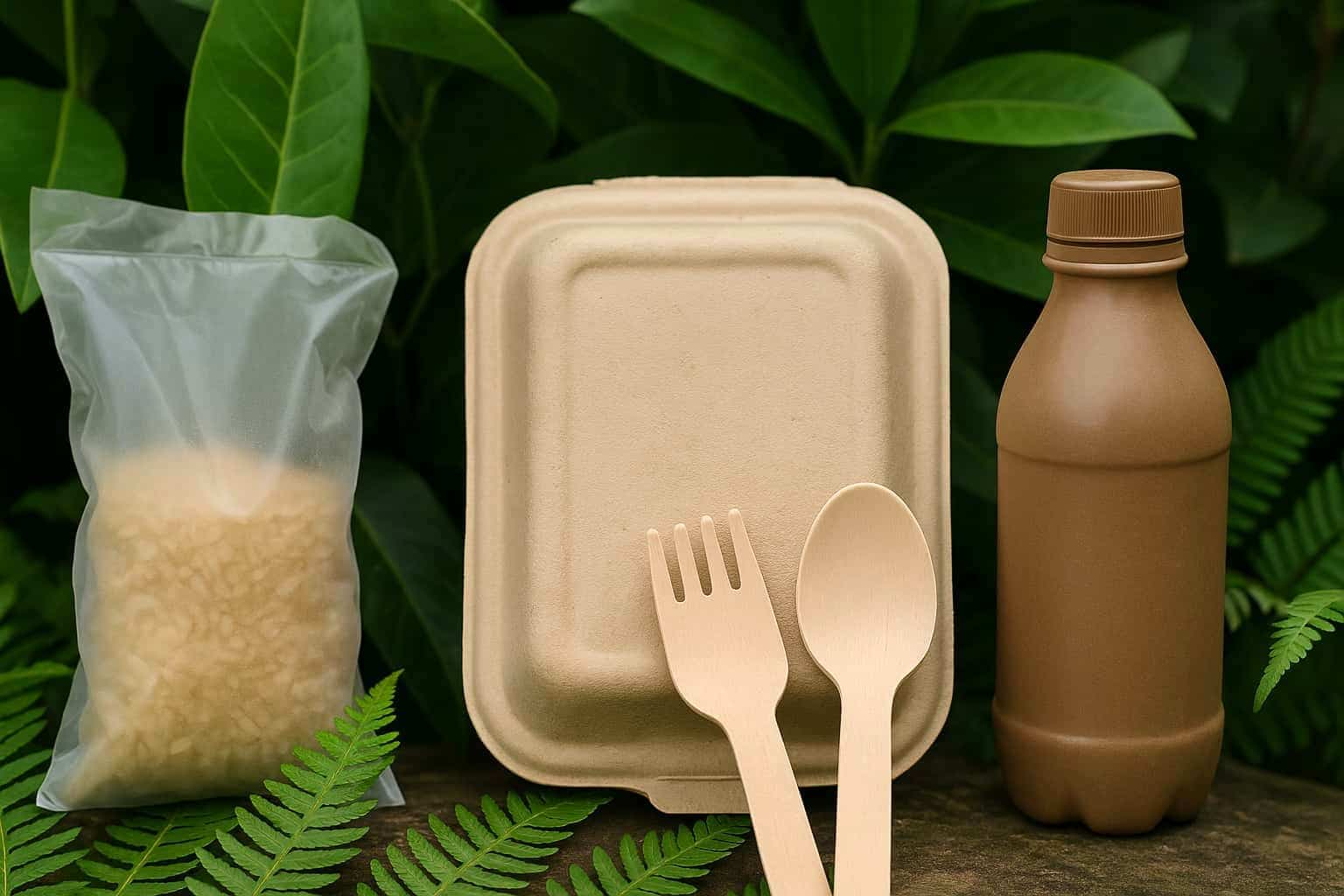
As more companies look for ways to reduce plastic waste and become more environmentally friendly, biobased vs biodegradable materials are getting more attention. These two terms may sound similar, but they mean different things – and choosing the right one can make a big difference for your business. In this guide, you’ll learn what each material is, how they compare, where they are used, and what trends are shaping the future. You’ll also find simple, practical steps to help your business start using eco-friendly materials with confidence.
1. What Are Biobased Materials?
Biobased materials are made from renewable natural sources like plants, crops, or agricultural waste instead of fossil fuels such as oil or gas. Common sources include corn, sugarcane, soybeans, and wood. These materials are used to replace traditional plastics and reduce the environmental impact of everyday products.
For example, PLA (polylactic acid) is a popular biobased plastic made from corn starch. It’s often used in packaging, disposable tableware, and even 3D printing. Another example is biobased polyethylene, which is made from sugarcane and used in bottles and plastic bags. Some natural fibers like hemp and flax are also considered biobased and are used in textiles or construction materials.
When comparing biobased vs biodegradable, it’s important to understand that biobased refers to the source of the material, not its behavior after disposal. A biobased plastic may not break down naturally unless it is specifically designed to do so.
This distinction between biobased vs biodegradable is essential when evaluating sustainable materials. While biobased products reduce reliance on fossil fuels, their environmental impact also depends on how they are managed at the end of their life cycles.
2. Understanding Biodegradable Materials
Biodegradable materials are substances that can be broken down by natural processes – like bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms – into natural elements such as water, carbon dioxide, and organic matter. This breakdown usually happens over time and depends on environmental conditions like heat, moisture, and oxygen.
Unlike traditional plastics, which can take hundreds of years to decompose, biodegradable materials are designed to degrade within months or a few years. This makes them an attractive choice for businesses looking to reduce their environmental impact.
A key thing to understand is that biodegradable doesn’t always mean the product is made from natural or renewable sources. Some biodegradable plastics, for example, are derived from petroleum-based compounds but are engineered to break down faster than regular plastics.
For businesses, understanding this distinction is crucial when selecting materials that align with sustainability goals. While both options aim to reduce environmental harm, they serve different purposes and behave differently during and after use.

3. Biobased vs Biodegradable: Key Differences
In this section, we’ll explore the key differences between biobased vs biodegradable materials in a detailed comparison table to help you make informed choices for your products or packaging.
| Biobased | Biodegradable | |
| Source | Renewable (e.g., corn, sugarcane, starch) | Can be natural or petroleum-based |
| End-of-life behavior | May or may not degrade easily, depending on the formulation | Designed to break down into harmless substances under the right conditions |
| Environmental focus | Reduces reliance on fossil fuels | Reduces waste and pollution by decomposing naturally |
| Examples | PLA (polylactic acid), biobased PE | Compostable bags, starch-based packaging, some bioplastics |
| Compostability | Not always compostable | Often compostable, especially under industrial conditions |
| Recyclability | Can be recyclable depending on type | Biodegradable plastics are usually not recyclable |
| Usage Confusion | Often confused with biodegradable due to the “bio” prefix | Misunderstood as always eco-friendly, but depends on degradation conditions |
4. Applications of Biobased and Biodegradable Materials for Businesses
As sustainability becomes a global priority, many industries are shifting to biobased vs biodegradable materials. Here are common applications where businesses are making the switch:
Packaging Industry
- Biodegradable packaging includes compostable bags, trays, and films that break down after use, reducing landfill waste.
- Biobased materials like PLA and bio-PE are used to make rigid and flexible packaging.
Food and Beverage
- Biodegradable cutlery, cups, and containers made from cornstarch or bagasse are popular in restaurants and catering.
- Biobased alternatives offer food-safe, renewable options for bottles, jars, and wraps.
Agriculture
- Biodegradable mulch films and plant pots help reduce plastic use and simplify soil preparation.
- Biobased fertilizers and seed coatings also support eco-friendly farming.
Retail and E-commerce
- Biodegradable mailers and biobased shopping bags are being adopted to reduce plastic waste.
- Some fashion brands use biobased textiles like polylactic acid fibers or bio-nylon.
Healthcare
Biobased and biodegradable materials are used for disposable gloves, trays, and packaging to lower medical waste in hospitals and clinics.
Construction
Companies use biobased insulation, adhesives, and biodegradable formworks to meet green building standards.
By understanding these practical uses of biobased vs biodegradable materials, businesses can align their choices with environmental goals while meeting customer demand for eco-friendly products.

5. Future Trends in Biobased and Biodegradable Materials
The biobased vs biodegradable plastics market is currently undergoing rapid transformation as industries respond to growing environmental concerns, stricter regulations, and rising consumer demand for sustainable alternatives. According to Future Market Insights, here are some key trends shaping the future of this market:
Sustainability and Environmental Awareness
The market’s expansion from 2020 to 2024 was largely driven by increasing awareness of plastic pollution, climate change, and the environmental impact of petroleum-based plastics. Businesses began shifting toward biodegradable and compostable materials to align with corporate sustainability goals and meet the expectations of environmentally conscious consumers.
Regulatory Support and Global Policy Alignment
Stricter plastic waste reduction laws, coupled with global frameworks like the EU Green Deal and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), pushed companies across packaging, agriculture, automotive, and consumer goods industries to adopt greener materials. These policies helped accelerate investment and innovation in sustainable plastic alternatives.
Consumer Demand for Green Alternatives
Rising consumer preference for recyclable, compostable, and non-toxic materials played a major role in shaping the market. Brands across multiple sectors introduced eco-friendly products in response to pressure from customers, advocacy groups, and sustainability pledges.
Innovation in Bioplastic Materials
Advancements in polymer science led to the development of materials such as PLA (polylactic acid), PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates), starch-based plastics, and cellulose-derived biopolymers. These newer materials offered better biodegradability, strength, flexibility, and thermal resistance – expanding their applications in industries like food packaging, personal care, and healthcare.
Government Support and Infrastructure Investment
Governments responded by investing in composting systems, offering tax incentives for bioplastic manufacturers, and funding R&D into sustainable packaging. These initiatives laid the foundation for long-term industry growth and improved public trust in biodegradable products.
Technological Advancements for 2025–2035
Looking ahead, the market is expected to benefit from cutting-edge developments in biopolymer chemistry, enzyme-based degradation, and AI-assisted material design. Waste-to-bioplastic technologies and synthetic biology will further improve material quality and affordability, making bioplastics more competitive on a global scale.
Smart and Circular Packaging Solutions
Next-generation bioplastics will feature embedded tracking technologies and be compatible with closed-loop recycling systems, helping reduce waste and support circular economy goals. These innovations will drive smarter, more responsible product life cycles.
6. Choosing the Right Material for Your Business
Selecting between biobased vs biodegradable materials can be a turning point in your sustainability journey, but making the right choice depends on your industry, product goals, and environmental commitments.
Understand Your Product Lifecycle
Begin by analyzing your product’s lifecycle, from production to end-of-life disposal. Biobased materials, derived from renewable sources such as corn starch or sugarcane, are ideal when reducing carbon footprint is a priority. They’re especially useful in packaging, textiles, and consumer goods where sustainability messaging enhances brand value.
On the other hand, biodegradable materials are most effective when product disposal is a key concern. These materials break down naturally under certain conditions, making them suitable for single-use items like food packaging, agricultural films, and disposable cutlery.
Consider Regulatory and Certification Standards
Ensure the materials you choose comply with industry standards and regional regulations. Look for certifications such as OK compost, BPI-certified compostable, or USDA Certified Biobased to validate environmental claims. These not only support compliance but also build trust with eco-conscious consumers.
Balance Performance with Sustainability
While eco-friendliness is essential, it should not come at the expense of functionality. Evaluate how each material performs under real-world conditions, such as moisture, temperature, and durability. Collaborate with suppliers who provide technical data and sample testing to assess product performance before full-scale implementation.
Factor in Cost and Availability
The cost of switching to biobased or biodegradable materials can vary. Consider long-term benefits such as enhanced brand image, customer loyalty, and compliance with environmental regulations when calculating ROI. Additionally, check the supply chain reliability of the materials to avoid disruptions in your operations.
Tailor to Your Brand’s Sustainability Goals
Align your choice with your broader sustainability goals. For example, if your brand focuses on reducing fossil fuel use, biobased materials may be more appropriate. If minimizing landfill waste is your primary goal, biodegradable or compostable options are likely the better fit.

7. Practical Steps for Businesses to Adopt Eco-Friendly Materials
Transitioning to eco-friendly materials like biobased vs biodegradable options doesn’t have to be overwhelming. With the right strategy, your business can reduce its environmental impact while maintaining product quality and customer satisfaction. Here are practical steps to help you get started:
Step 1. Conduct a Material Audit
Start by reviewing the materials currently used in your products or packaging. Identify which components can be replaced with biobased or biodegradable alternatives without compromising functionality or compliance.
Step 2. Set Clear Sustainability Goals
Define what “eco-friendly” means for your business. Is your priority reducing fossil fuel use, lowering plastic waste, or meeting specific environmental certifications? This will guide your material choices.
Step 3. Work with Certified Suppliers
Choose suppliers that provide verified biobased vs biodegradable materials. Look for certifications like USDA Certified Biobased, TÜV Austria’s OK Compost, or EN 13432 to ensure product claims are credible and meet international standards.
Step 4. Run Pilot Tests
Before a full-scale rollout, test new materials in small batches. Evaluate performance, durability, and consumer feedback to ensure the transition doesn’t affect product usability or satisfaction.
Step 5. Train Your Team
Educate internal teams such as product development, procurement, and marketing on the differences between biobased vs biodegradable materials. This helps align decisions with sustainability goals and avoids greenwashing.
Step 6. Communicate Clearly with Customers
Use packaging labels, website content, or point-of-sale materials to inform customers about your eco-friendly efforts. Transparency builds trust and reinforces your brand’s commitment to sustainability.
Step 7. Monitor and Improve
Track the environmental and business impact of your new materials. Stay updated on market trends and regulatory changes so you can continue evolving your strategy over time.
8. Conclusion
As the world moves toward greener solutions, understanding the difference between biobased vs biodegradable materials is essential for businesses aiming to reduce environmental impact. While each offers unique advantages, choosing the right one depends on your product goals, industry, and sustainability targets.
As eco-conscious manufacturing continues to grow, companies that adopt greener materials early will not only reduce their environmental footprint but also meet rising consumer expectations and regulatory demands.
EuP Egypt, a leading provider in the world plastics market, offers high-performance biodegradable solutions, including biofillers and bioplastic compounds, engineered to support sustainable product development without compromising quality.
Partner with EuP Egypt to make your transition to eco-friendly materials seamless and successful. Contact us today to explore our biodegradable product range and discover how we can support your sustainability journey.