Ever wondered why flexible packaging films lose clarity, stick together, or fail to seal properly? The answer often lies in the right plastic additives for flexible packaging films. In this guide, we’ll explain the major additive types, how to select them wisely, and why they matter for modern packaging.
1. Why Additives Matter in Flexible Packaging
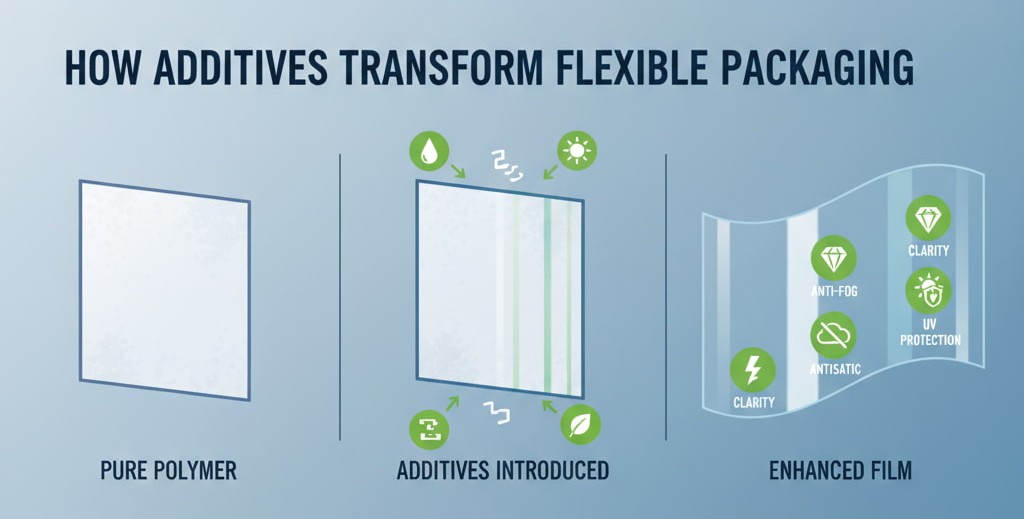
Ever wondered why plastic packaging sometimes loses clarity, sticks together, or tears too easily? The answer often lies in the right additive formulation.
Pure polymers like PE or PP can be brittle, sticky, or degrade under heat and light. Additives are what transform these basic resins into high-performance flexible films that run efficiently on machines, protect products, and look appealing on shelves.
In flexible packaging, every property counts:
- Clarity ensures visibility and appeal.
- Slip allows easy unwinding and sealing.
- Anti-fog keeps food fresh and visible.
- Antistatic prevents dust buildup.
Additives help fine-tune each property — turning plain polymer into packaging that performs.
2. Major Categories of Additives Used in Flexible Packaging Films
Every flexible packaging film relies on a careful mix of additives to deliver the right balance of strength, clarity, and flexibility. Below are the most common additive types and what they do to improve performance and production efficiency.
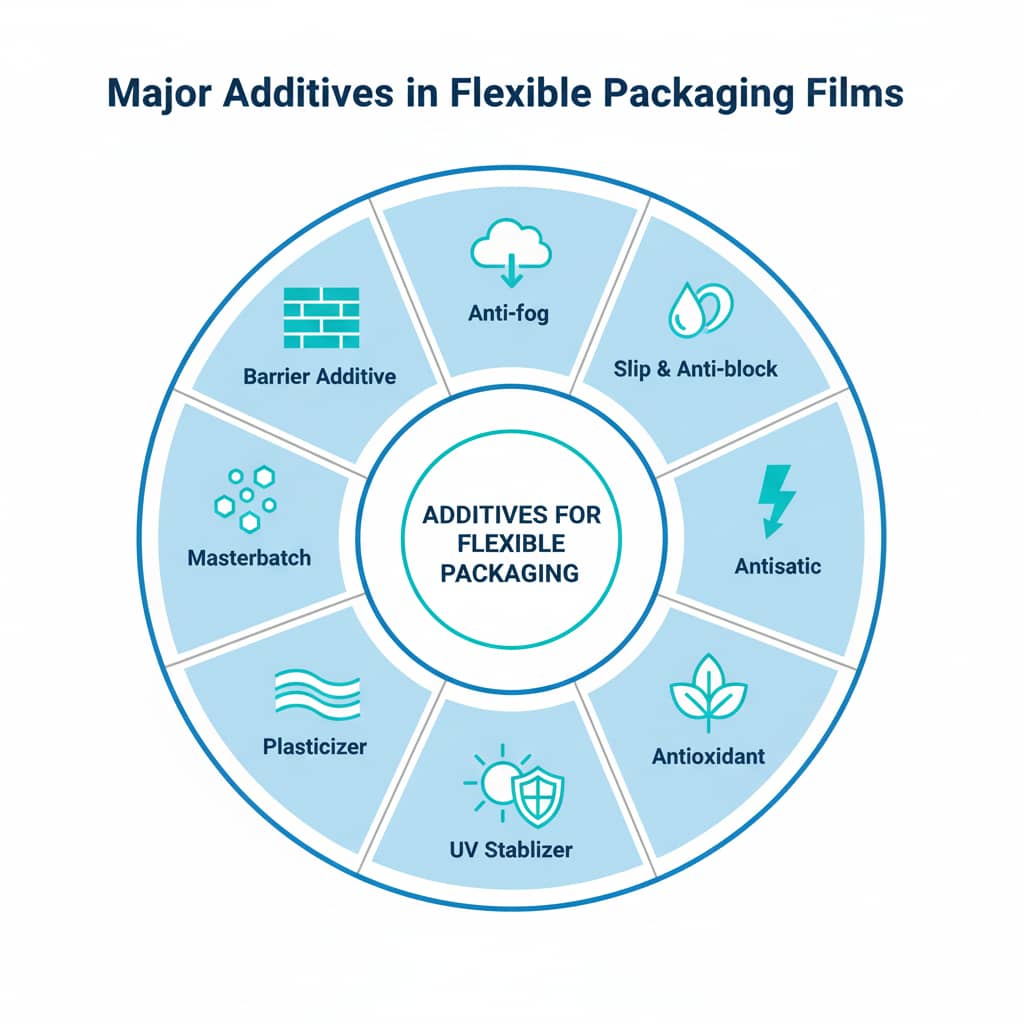
2.1. Slip agent and anti-block agents
If you’ve ever peeled apart two plastic sheets that stick together, you’ve seen why slip and anti-block agents matter. These additives reduce friction between film layers, making them easier to handle, wind, or open.
- Slip agents — often made from fatty acid amides like erucamide or oleamide — migrate to the film’s surface, forming a thin lubricating layer.
- Anti-block agents, such as silica or talc, create microscopic roughness that keeps films from sticking.
They are widely used in PE and PP films for snacks, laminations, and industrial wraps. However, too much slip can cause haze or affect coefficient of friction over time, so balancing the formulation is key.
2.2. Anti-fog and anti-condensation additives
In cold or humid environments, condensation can ruin product visibility and even shorten shelf life. Anti-fog additives solve this by changing the film’s surface tension, helping water spread evenly instead of forming droplets.
These additives are essential for food packaging films like fresh produce wraps or refrigerated trays. They keep packaging clear, ensuring consumers can see the product inside.
Modern solutions are moving toward non-migratory anti-fog agents, which last longer and work well in multilayer films used for complex packaging structures.
2.3. Antistatic additives
Static electricity may seem harmless, but in packaging production, it attracts dust and causes serious handling issues. Antistatic additives prevent this by allowing charge to dissipate safely.
They often contain glycerol monostearate or ethoxylated amines, which create a conductive layer on the film’s surface. These agents are highly compatible with PE, PP, and BOPP films, common in consumer packaging.
With growing demand for eco-friendly solutions, manufacturers are now turning to vegetable-based permanent antistatic agents, which deliver the same performance without migration or toxicity concerns.
2.4. Antioxidants and heat stabilizers
During film extrusion, high heat and oxygen exposure can break polymer chains, leading to discoloration, brittleness, and loss of strength. Antioxidants and heat stabilizers prevent this degradation.
- Primary antioxidants (e.g., hindered phenols) neutralize free radicals.
- Secondary antioxidants (e.g., phosphites) decompose peroxides.
Together they maintain film strength, color, and sealing performance. Proper stabilizer selection reduces yellowing, rejects, and downtime — especially in high-speed blown film lines.
2.5. UV Stabilizers and Light Protection Additives
Films used outdoors or in transparent packaging face damage from sunlight. UV stabilizers, including HALS (hindered amine light stabilizers) and UV absorbers, protect against this.
They prevent color fading, maintain film flexibility, and extend the lifespan of products like agricultural mulch films, greenhouse covers, or transparent food wraps.
With growing recycling demands, newer stabilizers are also designed to be non-migratory, avoiding contamination in recycled resins.
2.6. Plasticizers and Impact Modifiers
Some films, especially PVC-based or specialty polymer films, need plasticizers to stay flexible and soft. These additives reduce brittleness and improve impact resistance, especially in cold environments.
Traditional plasticizers were phthalate-based, but the industry is moving toward non-toxic, phthalate-free alternatives such as citrates and adipates.
They make packaging films more compliant with food-contact and medical regulations while maintaining elasticity and durability.
2.7. Filler masterbatch, pigment and clarifying agents
Additives aren’t only about performance — they also improve the look and cost of films.
- Calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) filler masterbatch lowers resin use, increases stiffness, and reduces costs.
- Color masterbatch ensures consistent shades and opacity.
- Clarifying agents (e.g., sorbitol-based) enhance transparency and gloss.
For converters, these additives help balance aesthetics, strength, and cost — essential for competitive markets like consumer packaging.
Read more: Filler Masterbatch for Food Packaging: Boosting Efficiency & Reducing Production Cost

2.8. Barrier enhancers and scavengers
Flexible packaging often needs to block oxygen, moisture, or odors. That’s where barrier additives and scavengers come in.
- Oxygen scavengers remove residual O₂ to prevent oxidation.
- Nanoclay or EVOH-based barriers limit moisture and gas permeability.
These additives are critical in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic packaging, where even a small oxygen leak can shorten product lifespan.
Each of these additives plays a specific role, but the best results come from combining them strategically.
Quick Summary Table
| Additive Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Slip & Anti-block | Reduce friction, prevent sticking |
| Anti-fog | Prevent condensation |
| Antistatic | Reduce dust attraction |
| Antioxidant & Stabilizer | Prevent degradation |
| UV Stabilizer | Protect from sunlight |
| Plasticizer | Add flexibility |
| Filler Masterbatch | Lower cost, improve stiffness, elongation |
| Barrier Additives | Extend shelf life |
4. Selecting the Right Additive Package for Flexible Films
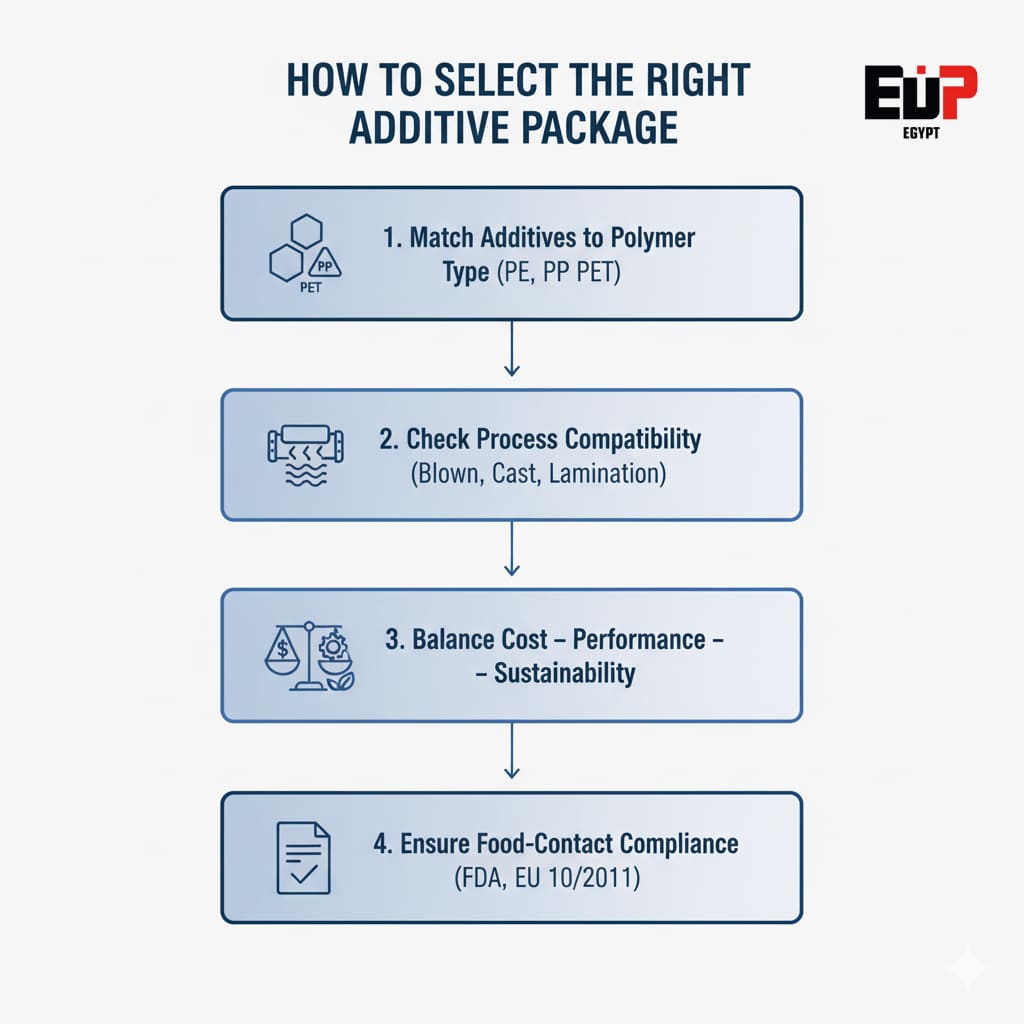
Choosing the right combination of additives can make or break the performance of your film. It’s not just about adding more ingredients — it’s about finding the right balance for your polymer, process, and end-use application.
4.1 Match Additives to Polymer Type
Every polymer behaves differently. Polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and PET each have their own structure, melting point, and compatibility level with additives.
For example, slip agents migrate faster in LDPE than in BOPP films because of different surface energies. Meanwhile, antioxidants that work perfectly in PP may lose efficiency in PET at higher temperatures.
That’s why formulating additive masterbatch starts with understanding the base resin. Using the right carrier ensures even dispersion and prevents unwanted reactions during extrusion.
4.2 Process and Equipment Compatibility
Additives must perform not only in the product but also during processing. Film blowing, casting, and lamination all apply different levels of heat and shear.
A stabilizer that works in low-temperature casting might degrade under high-speed blown film extrusion. Similarly, fillers that aren’t well-dispersed can clog screens or cause film breakage.
To avoid downtime, manufacturers test additives under real production conditions — matching particle size, melting index, and processing temperature.
The right additive package helps films flow better, reduce die build-up, and improve winding performance without compromising film quality.
4.3 Balancing Cost, Performance, and Sustainability
More additives don’t always mean better results. Overloading a film can lead to haze, stickiness, or weak sealing. On the other hand, using too little can hurt performance and increase waste.
Successful converters know how to balance three key factors:
- Cost efficiency: Replace a portion of resin with fillers to reduce expenses.
- Performance: Use multifunctional additives that improve several properties at once.
- Sustainability: Choose low-migration or bio-based solutions that support recyclability.
Smart formulations use filler masterbatch or additive blends to simplify dosing while maintaining mechanical strength and clarity.
4.4 Food-Contact and Regulatory Compliance
For films touching food, safety is critical. Additives must meet global regulations such as:
- FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 (U.S.)
- EU 10/2011 (Europe)
- GB 4806 (China)
Testing confirms that migration levels stay within safe limits under heat and humidity. Partnering with certified suppliers protects both consumers and brand integrity.
EuP Egypt’s food-grade additive masterbatches are manufactured under ISO 9001 and 14001 quality systems, ensuring consistent compliance and traceability.
5. FAQs About Plastic Additives for Flexible Films
- What are the most common additives used in flexible packaging films?
The most widely used are slip and anti-block agents, antistatic additives, anti-fog agents, antioxidants, and UV stabilizers. Each serves a different purpose.
- Are these additives safe for food contact?
Yes, when properly formulated. Additives for food-contact packaging must meet strict regulations such as FDA or EU 10/2011. Reputable suppliers offer food-grade masterbatches designed to ensure low migration and non-toxicity.
- Do additives affect recyclability?
They can, depending on the type and amount. Migrating additives may affect recycling streams, but modern non-migratory and eco-compatible solutions maintain polymer purity for circular economy goals.
- Can one additive provide multiple benefits?
Absolutely. Multifunctional masterbatches combine roles — like slip + antiblock or UV + antioxidant systems — reducing cost and improving efficiency.
- How are additives introduced — via masterbatch or direct dosing?
Most are added via additive masterbatch for uniform dispersion and cleaner processing. Direct powder dosing is rarely used today due to dust and mixing issues.
6. Conclusion
In flexible packaging, performance isn’t just about the polymer — it’s about the additives working behind the scenes. From anti-fog to antioxidants, every additive plays a key role in achieving clarity, strength, and shelf stability.
Choosing the right additive package means balancing performance, cost, and sustainability. As packaging moves toward recyclability and lower carbon impact, innovative additive technologies will continue driving efficiency and environmental responsibility.
7. About EuP Egypt
At EuP Egypt, we’re more than just a material supplier — we’re a partner in performance.
As part of EuP Group, one of the world’s leading masterbatch and compound manufacturers, EuP Egypt specializes in delivering high-quality filler masterbatch, color masterbatch, and additive solutions tailored for flexible packaging applications.
🏭 Factory & Capacity:
- 34,000 m² facility in Sadat City, Egypt
- 300,000 tons/year production capacity
🌍 Markets Served:
Africa | Middle East | Europe | Americas
Our mission is to help packaging manufacturers create stronger, smoother, and more sustainable films through advanced masterbatch solutions.
Whether you need slip + antiblock blends, antioxidant masterbatches, or bio-based additives, EuP Egypt delivers proven performance backed by global expertise.

📩 Contact us today to discover how our customized additive technologies can enhance your flexible packaging films — from clarity and strength to sustainability.





